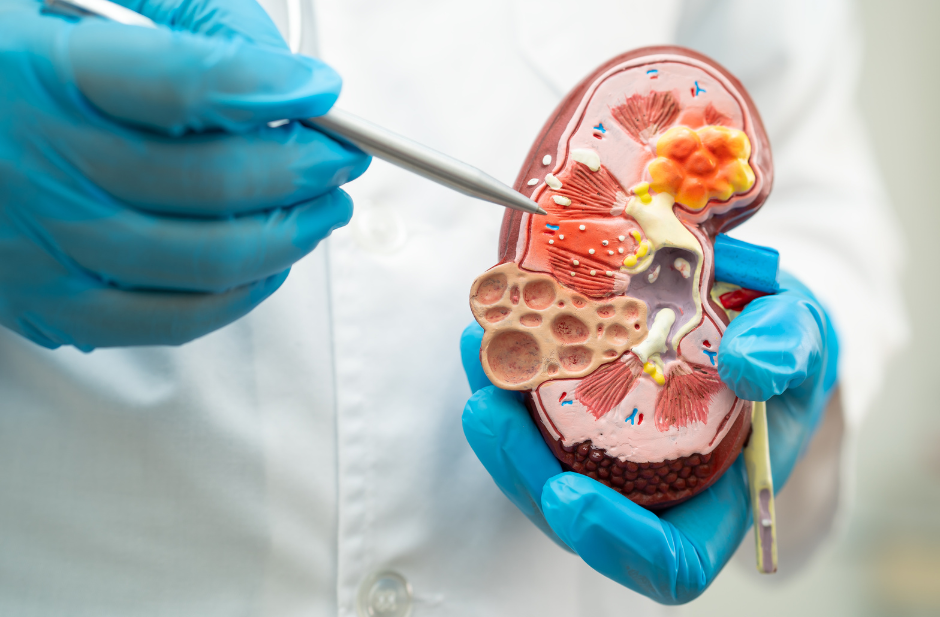
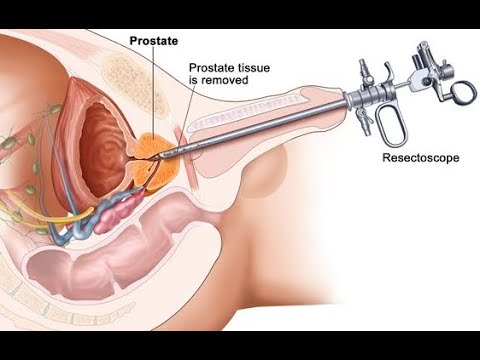
Prevention of stones
Preventing kidney stones often involves lifestyle and dietary modifications aimed at reducing the risk factors associated with stone formation. Here are some key strategies for preventing kidney stones:
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, throughout the day to maintain urine volume and dilution, which can help prevent the formation of kidney stones. Aim to drink enough fluids to produce at least 2 to 2.5 liters (about 8 to 10 cups) of urine per day, unless otherwise advised by your doctor.
Limit Sodium Intake: High sodium intake can increase the excretion of calcium in urine, which can contribute to the formation of calcium-containing kidney stones. Aim to limit your daily sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams (about one teaspoon of salt) per day.
Moderate Protein Consumption: Diets high in animal protein, especially red meat, can increase the risk of certain types of kidney stones. Aim for moderate consumption of protein and consider incorporating plant-based protein sources such as legumes, nuts, and tofu.
Reduce Oxalate-rich Foods: Some kidney stones are composed of calcium oxalate. Limiting the consumption of foods high in oxalate, such as spinach, rhubarb, nuts, tea, and chocolate, may help reduce the risk of calcium oxalate stone formation.
Limit Foods High in Purines: If you have a history of uric acid stones, it's important to limit foods high in purines, such as organ meats, shellfish, and certain types of fish, as they can increase uric acid levels in the urine.
Increase Dietary Calcium: Contrary to popular belief, adequate intake of dietary calcium may actually reduce the risk of calcium oxalate stones by binding with oxalate in the intestine and reducing its absorption into the bloodstream. Choose calcium-rich foods such as low-fat dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity and excess weight can increase the risk of kidney stones. Aim to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Monitor Medications: Some medications can increase the risk of kidney stones. If you're taking medications that may contribute to stone formation, discuss alternative options with your healthcare provider.
Be Mindful of Supplement Use: Avoid excessive intake of vitamin C supplements, as large doses can be metabolized into oxalate in the body, potentially increasing the risk of kidney stones.
Follow Medical Advice: If you have a history of kidney stones or are at increased risk, follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for regular monitoring and preventive measures.